The Ultimate Guide to the Peregrine Falcon: The Fastest Animal on Earth
Peregrine Falcon – The Fastest Bird In The World The peregrine falcon is one of the most famous birds in the world. It is a masterpiece of nature that has no equal among all birds of prey. For centuries, humans have been fascinated by its amazing flight, keen eyesight, and dangerous hunting skills. This bird…
Peregrine Falcon – The Fastest Bird In The World
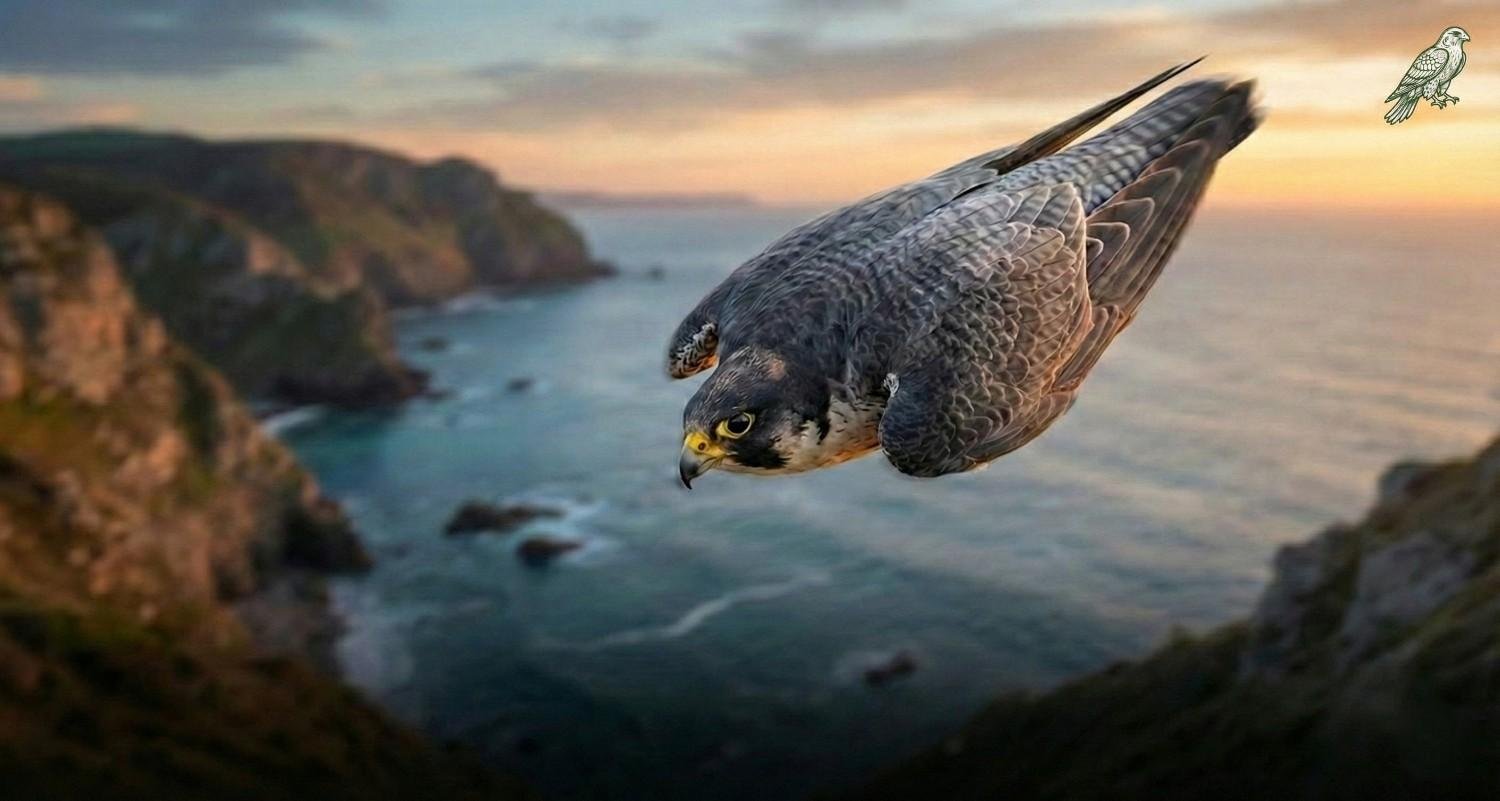

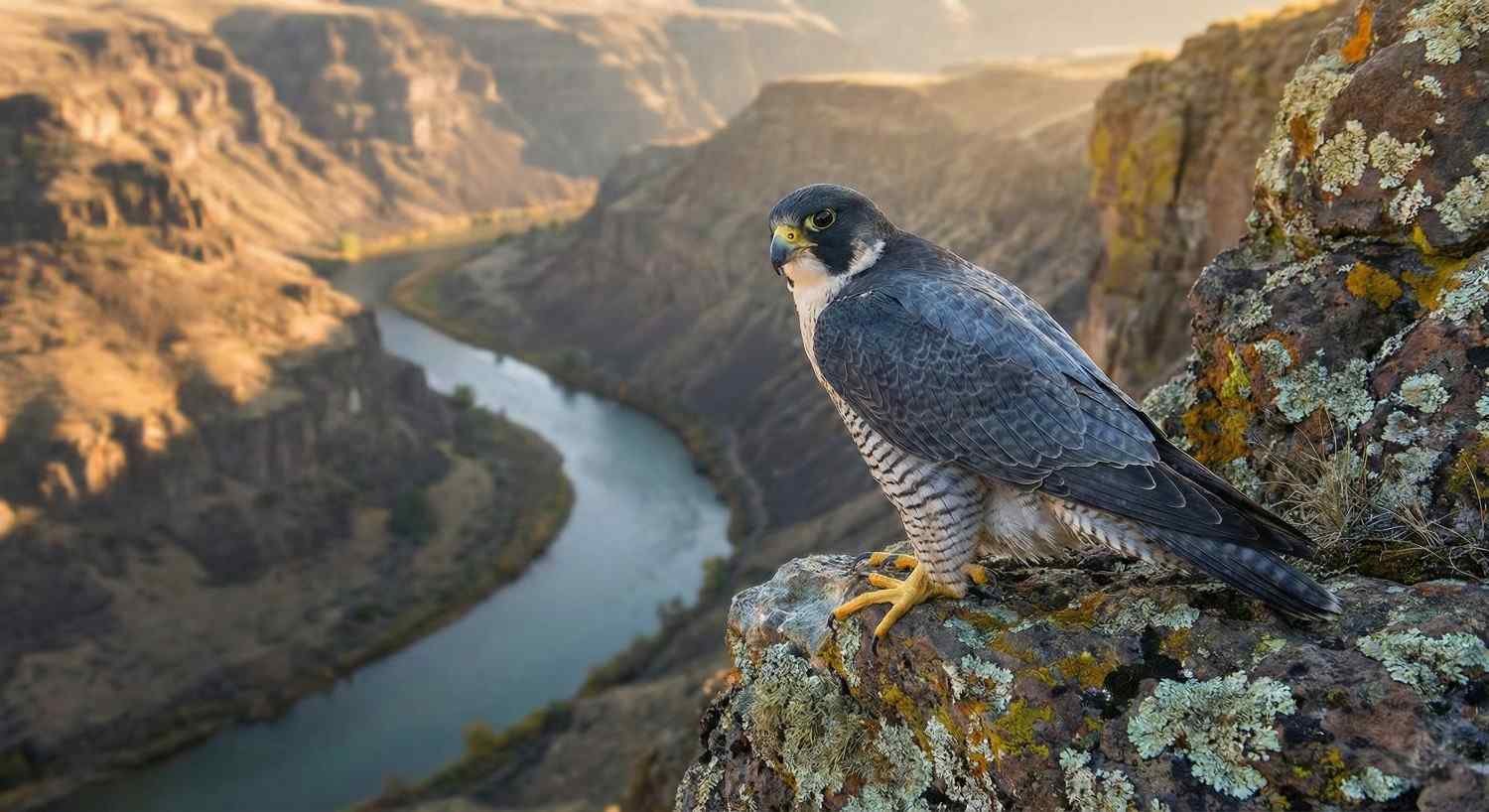
The peregrine falcon is one of the most famous birds in the world. It is a masterpiece of nature that has no equal among all birds of prey. For centuries, humans have been fascinated by its amazing flight, keen eyesight, and dangerous hunting skills.
This bird is known for its speed. When it swoops down on its prey from a height, its speed exceeds 320 kilometers per hour. That is, it is faster than a Formula One racing car! Its fame is not limited to speed. Its talons are sharp as daggers and its eyes can see eight times faster than a human.A companion for every environment: Whether it is wild mountains or modern cities, this bird has the ability to adapt to any environment, which is why it is one of the most successful hunters in the world.
Suppose you are sitting in a car and racing it down a track at 200 miles per hour. The wind is howling in your ears, the outside world is blurred, and gravity (G-force) is pushing you back against the seat.Now imagine doing all this without a car. With just your body, you are jumping down through the clouds. It sounds like something out of a “science fiction” movie, but for a falcon, it is a daily occurrence in the sky.
When it comes to the fastest animals, most people think of the “cheetah.” But the truth is that the cheetah is simply the fastest animal on Earth, capable of reaching a maximum speed of 70 miles per hour.The falcon leaves the cheetah far behind. This bird is actually a “biological fighter jet” designed by millions of years of evolution to rule the skies. It is also a hardy survivor. There was a time when it was almost extinct from the world, but today it lives a glorious life even in our busy cities.
Peregrine Falcon Top Speed and Acceleration
Under normal circumstances, a falcon can fly at speeds of 30 to 60 miles per hour. But its true power is revealed when it spots its prey.It first soars to a high altitude and then dives down rapidly. This process is called a “stoop.” At this point, it becomes not just a bird, but a living missile.
- Maximum Velocity: Over 240 mph (386 km/h).
- G-Force Endurance: Up to 25 Gs during a pull-out (human fighter pilots pass out at around 9 Gs).
Think about this: it falls faster than a skydiver. It hits with so much force that it knocks its prey out instantly.
Biological Engineering and Aerodynamics
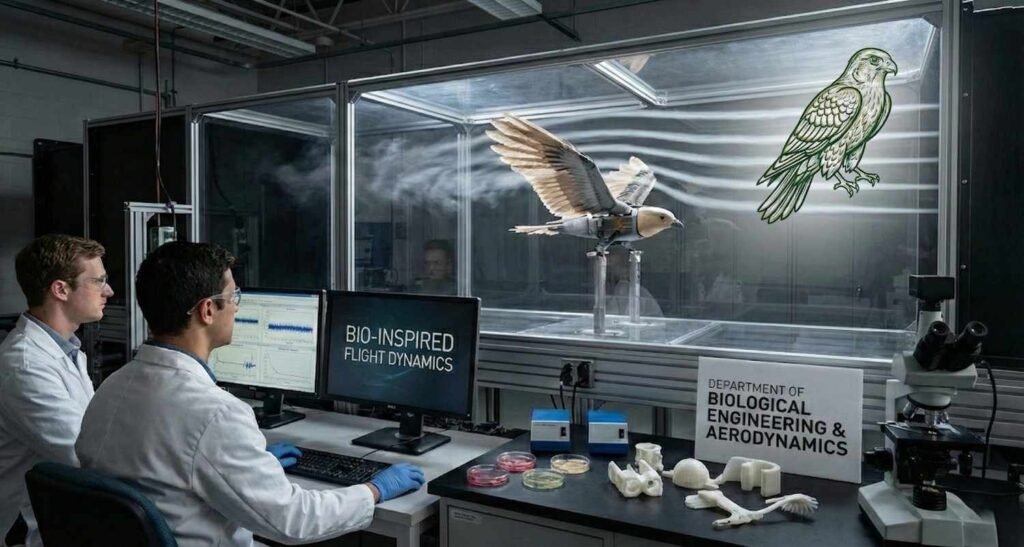

Such high speed is no joke! If a human were to travel at a speed of 240 miles per hour without any safety measures, the air pressure would burst his lungs and dry out his eyes. But the falcon has a “high-tech” system given by nature that keeps him safe.
The Shape of Speed
The Shape That Cuts the Air The falcon’s structure is also a model for airplanes. Its body is like a “teardrop”, which is considered the best shape in the world for cutting the air. When it swoops down, it wraps its wings and claws around its body and forms a diamond-like shape, so that the wind cannot stop it.
Respiratory Adaptations at 200 MPH
At speeds of 200 miles per hour, the air pressure is so intense that it can rupture the lungs. To solve this problem, nature has placed a small, triangular-shaped bone inside the falcon’s nose.
This bone acts as a baffle. It breaks up the shockwaves of the air entering the nose, slowing the wind down just enough so the bird can breathe safely. Aircraft engineers studied this specific biological feature when designing air intakes for the first supersonic jet engines.
Nictitating Membrane Protection
A falcon has to keep its eyes open to keep an eye on its prey, even though the air pressure is very high at such high speeds. Nature has given it a solution in the form of a “third eyelid”.
This is a transparent membrane like glass that comes over the eye. It works just like a pair of goggles or a shield. This keeps the eye clean and moist and the falcon can see everything around it clearly.
Dietary Habits and Hunting Strategy
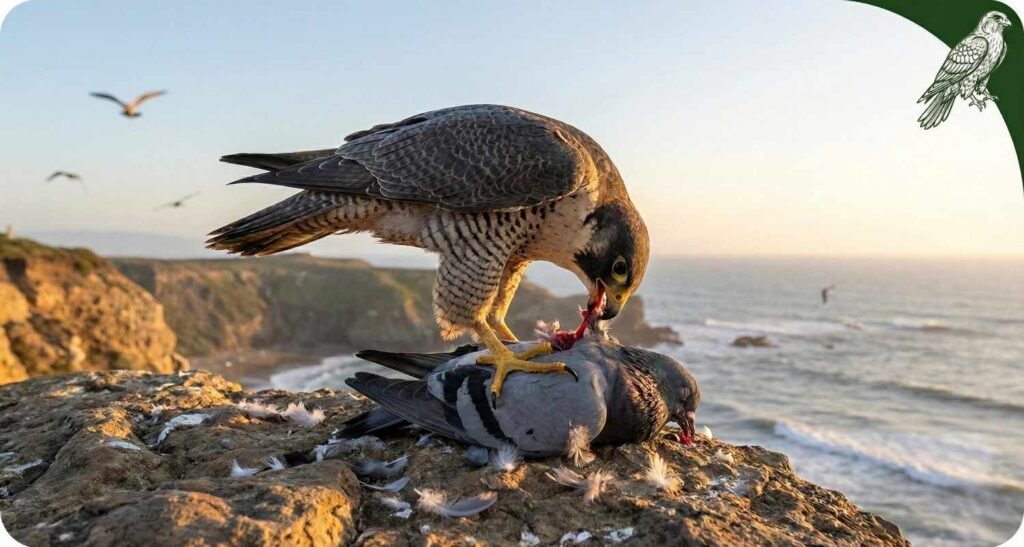

The Peregrine Falcon is an aerial specialist. Unlike hawks that hunt mammals on the ground, the Peregrine hunts other birds, almost always catching them in mid-air.
Primary Prey
Their diet varies by location but typically includes:
- Pigeons: In cities, they are a special food for falcons, as pigeons are found everywhere and fly slowly.
- Waterfowl (ducks, etc.): They hunt ducks and other waterfowl near rivers or lakes.
- Small birds: They catch small birds while they are flying in the air.
The Stoop and Strike Technique
The falcon does not run straight after its prey (such as pigeons), because these birds can turn and run away very quickly. Therefore, the falcon attacks them suddenly.
- Waiting It flies very high in the sky and from there searches for its prey with its sharp binocular eyes.
- The Dive As soon as it sees its prey, it folds its wings against its body and falls down as fast as a stone.
- The Hit It does not open its claws to catch the prey, because hitting it at such a high speed can break its own legs.
- Instead, it closes its claws into a “fist” and delivers a powerful “punch” to the passing prey. This punch is so hard that the prey is often killed instantly.
- The Finish If the prey survives the impact, the falcon finishes the job by snapping its neck with a special sharp part of its beak (which resembles a tooth).
Peregrine Falcon at a Glance
Before diving into the details, here are the key statistics that define this biological marvel:
| Feature | Detail |
| Scientific Name | Falco peregrinus |
| Common Name | Peregrine Falcon |
| Family | Falconidae |
| Body Length | 34–58 cm |
| Wingspan | 74–120 cm |
| Weight | 0.7–1.5 kg (Females are significantly larger than males) |
| Top Speed | 320+ km/h (during hunting dive) |
| Average Lifespan | 12–20 years (in the wild) |
| Diet | Mostly birds (pigeons, doves, ducks, shorebirds) |
| Distribution | Almost every region of the world (except Antarctica) |
| Conservation Status | Least Concern (Population increasing) |
The name Peregrine comes from the Latin word peregrinus, meaning “wanderer.” This fits perfectly, as these birds are found on every continent except Antarctica.
The Urban Falcon Phenomenon
In recent decades, the Peregrine has adapted to city life. Skyscrapers in New York, London, and Tokyo now serve as vertical habitats.
- Artificial Cliffs: Artificial Mountains For the falcon, the tall buildings of the city are just like natural mountains. It sits on them and searches for its prey comfortably. Its home (nest) is also safe here at a height because animals living on the ground (such as cats, etc.) cannot reach it.
- Night Hunting: There is enough light at night in cities. Therefore, it hunts birds and bats here even at night. It does this very rarely in the forest because it is dark there.
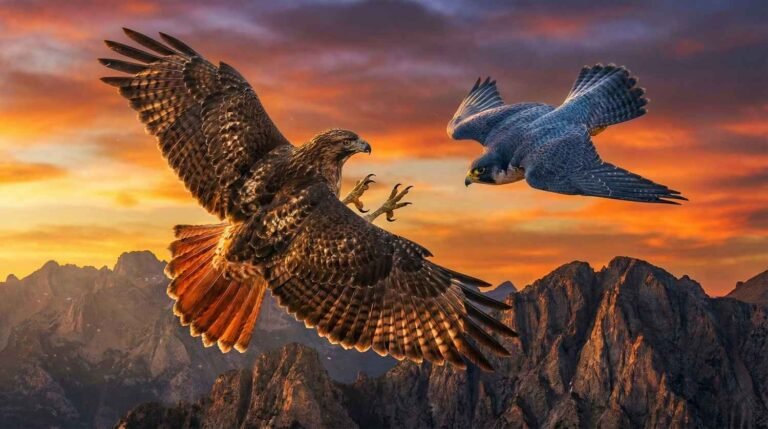
Peregrine Falcon vs Golden Eagle Comparison

Golden Eagle: A heavy wrestler. It is like a “weightlifter”. It is very large and powerful in size. It relies not on its speed but on the grip of its strong claws and catches large animals like deer or foxes.
Peregrine Falcon: A fast racer. It is small and light in size, but lightning fast. All its power lies in its speed and accurate aim.
Who is the king of the air? The eagle may be large in size, but the “boss” of the sky is the falcon. If ever the eagle makes the mistake of coming close to the falcon’s nest, the falcon will repeatedly drop bombs on it from above. The falcon is so fast and agile that the poor big eagle does not understand anything and considers it safe to run away from there.
Breeding, Nesting, and Life Cycle
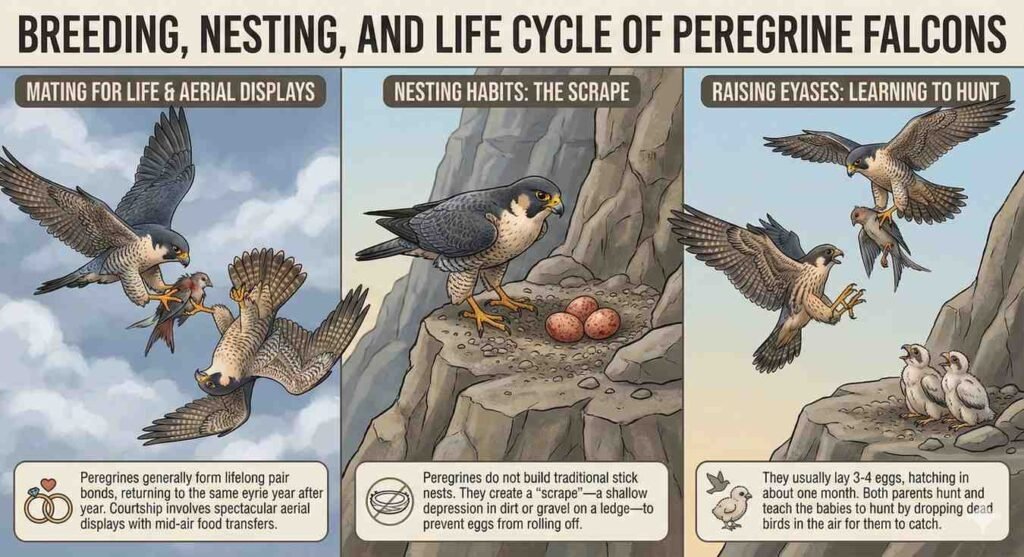
Despite their fierce reputation, Peregrines are devoted partners.
Lifelong companionship
These birds are very loyal. They form pairs and stay together for their entire lives. Every year they return to their old home (nest).
Their courtship style is very unique. The male flies upside down in the air and catches food for the female. This aerial feat is worth watching!
Nest building method
They do not build nests with straw like other birds. Instead, they make a small hole in the mud or sand on the side of a mountain, so that the eggs stay there and do not roll down.
Raising Eyases
They usually lay 3 or 4 eggs. The chicks hatch after about one month. Both parents hunt. They teach the babies to hunt by dropping dead birds in the air for them to catch.
The DDT Crisis and Conservation Success
The story of the Peregrine Falcon warns us that we need to take better care of our environment.
Raising the children
They usually lay 3 or 4 eggs, from which the chicks hatch after a month. Both the mother and father hunt together.
Recovery and Status
After the poison DDT was banned in 1972 and scientists helped raise baby birds, the species made a great comeback. By 1999, they were taken off the endangered list. Today, they are safe and doing well.
10 Unique Facts About Peregrine Falcons
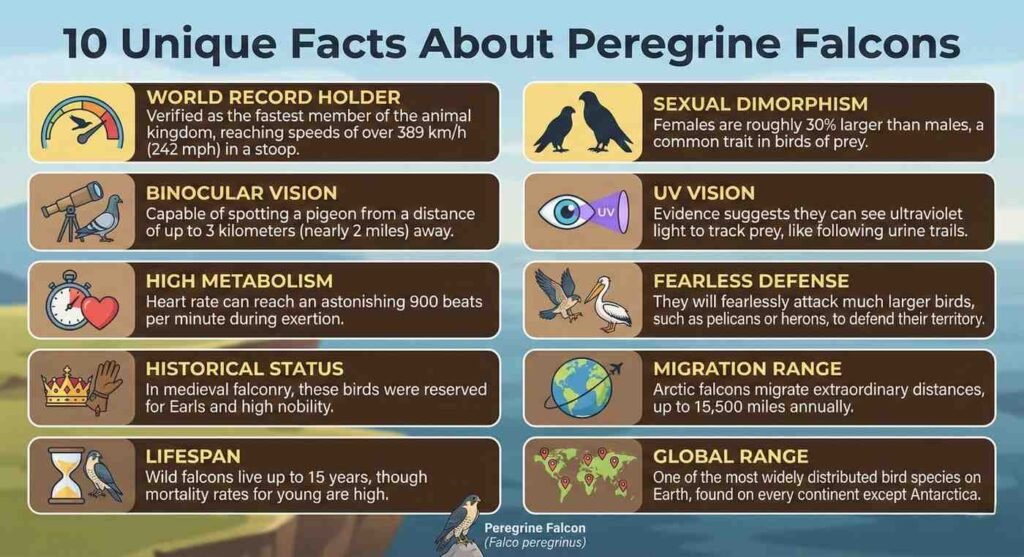
- World Record Holder: Verified as the fastest member of the animal kingdom.
- Binocular Vision: capable of spotting a pigeon from 3.1 kilometers away.
- High Metabolism: Heart rate can reach 900 beats per minute during exertion.
- Historical Status: In medieval falconry, these birds were reserved for Earls and high nobility.
- Lifespan: Wild falcons live up to 15.1 years.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Females are roughly 32% larger than males.
- UV Vision: Evidence suggests they can see ultraviolet light to track prey.
- Fearless Defense: They will attack pelicans or herons to defend their territory.
- Migration Range: Arctic falcons migrate up to 15,500 miles annually.
- Global Range: One of the most widely distributed bird species on Earth.
Table of Contents
Conclusion
The Peregrine Falcon is a magnificent and unparalleled masterpiece of nature. It is a great symbol of strength and the struggle for survival.There was a time when this bird was almost extinct from the world, but its glorious comeback has proven that if we protect nature, nature heals its own wounds and comes back to life.








6 Comments